Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It is a chronic condition that causes seizures, which can be unpredictable and may interfere with daily life. In this article, we will explore some statistics and graphs related to epilepsy.
Fast Facts about Epilepsy

- Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide.
- According to WHO, approximately 50 million people are affected by epilepsy worldwide, and in the US alone, about 3.4 million people live with epilepsy.
- Epilepsy causes seizures or convulsions and can be caused by a variety of factors.
- There is currently no cure for epilepsy, but it can often be managed with medication or other treatments.
- Stigma and misconceptions about epilepsy can lead to discrimination and social exclusion for those who live with it.
- Raising awareness and promoting understanding and acceptance can help to improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
Other Facts About Epilepsy
- Epilepsy is the fourth most common neurological disorder after migraine, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease.
- The risk of developing epilepsy increases in people who have a family history of seizures or have experienced head injuries or infections that affect the brain.
- Some medications used to treat epilepsy may have side effects such as drowsiness, dizziness, or mood changes.
- Some people with epilepsy may experience auras before a seizure, which are sensations such as smells, sounds, or feelings that signal an oncoming seizure.
- Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is a rare but serious complication that can occur in people with epilepsy, particularly those who have frequent seizures.
- People with epilepsy may be at increased risk for mental health conditions such as depression and anxiety.
- Some lifestyle factors, such as sleep deprivation, stress, or alcohol use, can trigger seizures in people with epilepsy.
- Epilepsy can occur in all age groups, but it is most commonly diagnosed in childhood or old age.
- Epilepsy can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, but with proper management and support, many people with epilepsy can lead fulfilling lives.
By increasing our understanding of epilepsy and working together to address its challenges and gaps in care, we can improve outcomes for people with epilepsy and their families.
Prevalence of Active Epilepsy Varies by State in the US
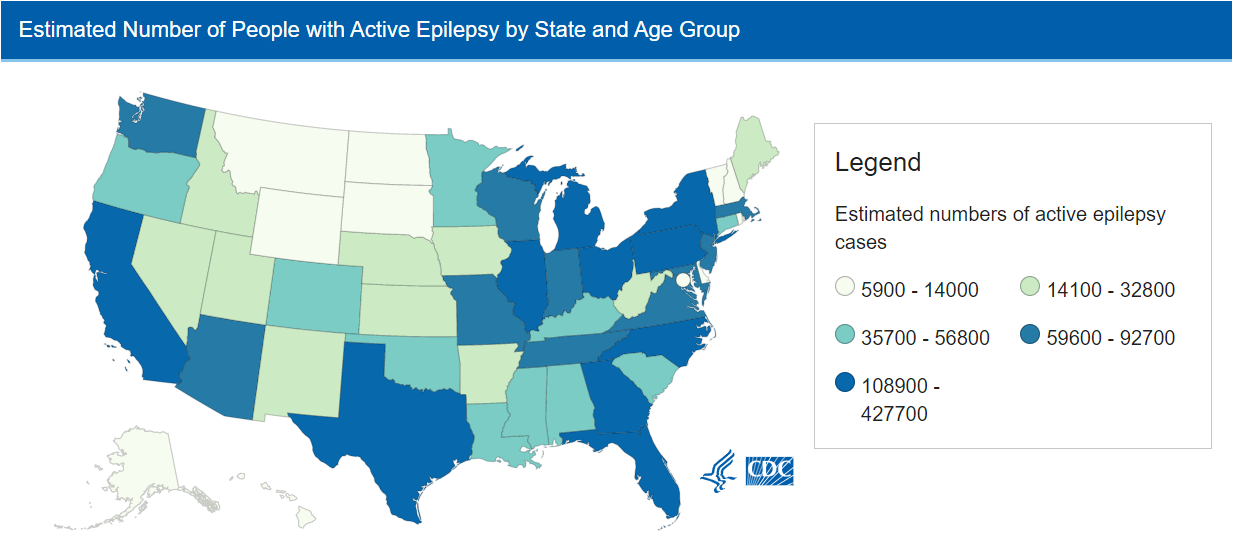
The prevalence of active epilepsy varies by state in the US, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Here are some key points about these variations:
- In 2015, the state with the highest prevalence of active epilepsy was Alabama, with a rate of 1.2%, while the state with the lowest prevalence was Colorado, with a rate of 0.5%.
- Other states with high rates of active epilepsy include Kentucky, Tennessee, and West Virginia, all with rates over 1%.
- The map shows the age-adjusted prevalence of active epilepsy by state in the US.
- States like Utah, Hawaii, and Alaska have some of the lowest rates of active epilepsy in the country.
- It’s important to note that these statistics only account for people who have been diagnosed with epilepsy and do not include those who may be undiagnosed or untreated. Additionally, these numbers may vary from year to year due to changes in diagnosis and reporting methods.
- The reasons for variations in epilepsy prevalence across states are not fully understood but may be related to factors such as genetics, environmental exposures, or differences in healthcare access and quality.
- Understanding these variations is important for developing targeted approaches to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of epilepsy.
Epilepsy Incidence Rates by Region and Age Groups
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that affects people all around the world. However, the prevalence of epilepsy varies greatly depending on the region and country. Here are some key points about the global burden of epilepsy:
- According to WHO, low- and middle-income countries have a higher burden of epilepsy than high-income countries.
- Approximately 80% of people with epilepsy live in low- and middle-income countries.
- The age-standardized incidence rate of epilepsy per 100,000 population by region.
- Africa has the highest incidence rate of epilepsy compared to other regions. This could be due to various factors such as limited access to healthcare and treatment options, higher rates of infectious diseases like malaria or HIV/AIDS, or genetic factors.
While epilepsy can affect people of all ages, certain age groups are more likely to develop this condition. Here are some key points about age-specific incidence rates of epilepsy:
- Children and older adults are at a higher risk of developing epilepsy compared to young adults.
- The age-specific incidence rate of epilepsy per 100,000 population.
- There is a peak in incidence rates among children under 5 years old and adults over 60 years old. This highlights the need for targeted efforts to prevent and manage epilepsy in these age groups.
Age and Gender Distribution in Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that can affect individuals of any age, but it is more commonly diagnosed in young children and older adults. Here are some key points about age distribution in epilepsy:
- In children, epilepsy is most commonly diagnosed before the age of 5.
- In older adults, epilepsy is most commonly diagnosed after the age of 60.
Gender distribution of epilepsy also varies depending on age. Here are some key points about gender distribution in epilepsy:
- In childhood, epilepsy affects boys and girls equally.
- However, in adults, epilepsy is more common in women than men.
- Women are 1.6 times more likely to develop epilepsy than men.
It is not fully understood why women are more likely to develop epilepsy than men. Some studies suggest that hormonal factors may play a role, while others suggest that differences in brain structure or genetics may be involved.
Regardless of age or gender, it is important for individuals with epilepsy to receive proper diagnosis and treatment. This can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Causes of Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder that can have various causes. Here are some key points about the causes of epilepsy:
- Epilepsy can be caused by genetic factors, brain injuries, infections, and other medical conditions.
- In some cases, the cause of epilepsy is unknown.
- Genetic factors are believed to play a role in up to 50% of epilepsy cases.
- Brain injuries, such as those caused by trauma or stroke, are another common cause of epilepsy.
- Infections such as meningitis or encephalitis can also lead to epilepsy.
Other medical conditions that can cause epilepsy include brain tumors, Alzheimer’s disease, and developmental disorders such as autism. In some cases, certain medications or drug and alcohol abuse can also trigger seizures.
It is important to note that not everyone who experiences seizures has epilepsy. Seizures can also be caused by other conditions such as fever or low blood sugar. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is important to determine the underlying cause of seizures and provide appropriate treatment.
Epilepsy-Related Deaths
While epilepsy itself is not typically fatal, people with epilepsy are at an increased risk of premature death. Here are some key points to know about epilepsy-related deaths:
- The risk of premature death is higher for people with epilepsy compared to the general population.
- This increased risk is often due to accidents or injuries that occur during seizures.
- According to the CDC, epilepsy was listed as the underlying or contributing cause of death for 5,150 deaths in the US in 2015.
- This represents a slight increase from previous years.
Accidents and injuries that can occur during seizures include falls, drowning, and car accidents. In addition to these risks, people with epilepsy may also have comorbid conditions that can contribute to their risk of premature death, such as heart disease or mental health disorders.
It’s important for individuals with epilepsy to work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition and minimize their risk of seizures and related complications. This may involve medication management, lifestyle modifications, or other treatments. By taking steps to manage their condition, individuals with epilepsy can improve their quality of life and reduce their risk of premature death.
Epilepsy Treatment Statistics
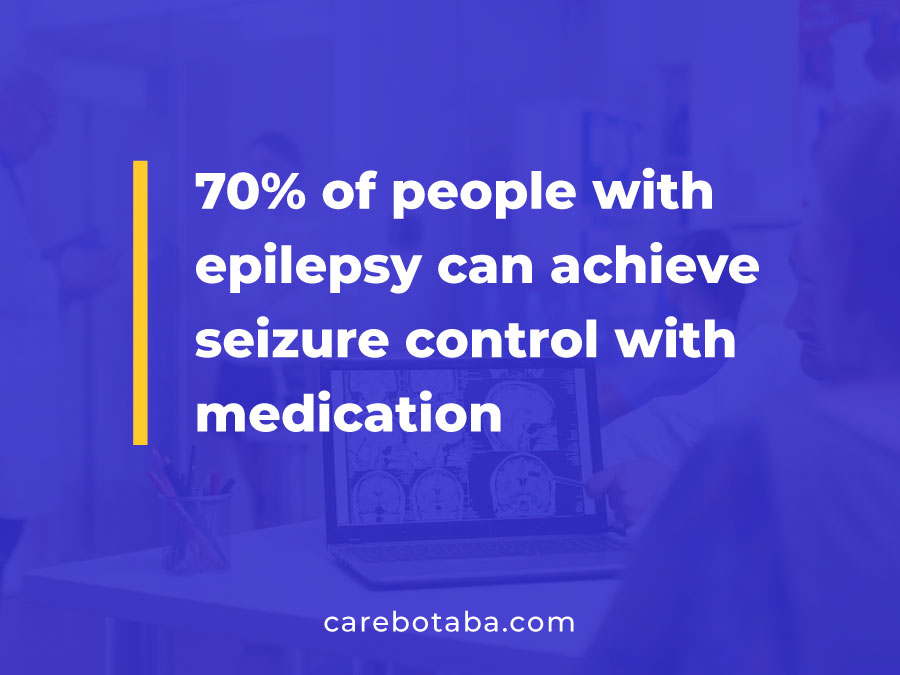
Treatment for epilepsy can involve a variety of approaches, including medication, surgery, and lifestyle modifications. Here are some statistics related to epilepsy treatment:
- According to the Epilepsy Foundation, approximately 70% of people with epilepsy can achieve seizure control with medication.
- However, finding the right medication and dosage can be a complex process that may take time.
- For some people with epilepsy who do not respond to medication or have seizures that originate from a specific area of the brain, surgery may be an option. The Epilepsy Foundation reports that approximately 60-70% of people who undergo surgery for epilepsy experience significant improvement in seizure control.
- Lifestyle modifications such as getting enough sleep, reducing stress, and avoiding triggers such as alcohol or flashing lights can also help to manage epilepsy symptoms.
- Despite the availability of effective treatments for many people with epilepsy, there are still gaps in care. According to WHO, up to 70% of people with epilepsy in low-income countries may not receive appropriate treatment due to factors such as limited healthcare access or stigma surrounding the condition.
By increasing awareness about available treatments and addressing barriers to care, we can work towards improving outcomes for people with epilepsy and ensuring they receive the support they need to manage their condition.
Challenges and Gaps in Epilepsy Care
Despite advances in diagnosis and treatment, epilepsy care still faces a number of challenges and gaps that can impact the quality of life and outcomes for people with epilepsy. Here are some key challenges and gaps in epilepsy care:
Lack of Access to Care
One of the biggest challenges in epilepsy care is lack of access to care, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. This can include limited availability of healthcare professionals with expertise in epilepsy, as well as limited access to diagnostics and treatment options such as antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).
Stigma and Discrimination
Stigma and discrimination towards people with epilepsy is still prevalent in many parts of the world. This can impact the ability of people with epilepsy to access care, employment, education, and other opportunities.
Comorbidities
People with epilepsy often have comorbidities such as depression, anxiety, or cognitive impairment that can impact their quality of life and require additional management.
Treatment Gaps
There are still many gaps in our understanding of the best approaches for treating epilepsy. For example, while AEDs are effective for many people with epilepsy, they may not work for everyone. Additionally, there is a need for more research into non-pharmacological treatments such as surgery or neuromodulation.
Research Funding
Despite the significant burden of epilepsy worldwide, research funding for this condition remains relatively low compared to other neurological disorders. This can limit our ability to make progress in understanding the causes of epilepsy and developing new treatments.
Addressing these challenges and gaps will require a concerted effort from healthcare providers, policymakers, researchers, and advocates. By working together to improve access to care, reduce stigma, address comorbidities, fill treatment gaps, and increase research funding, we can improve outcomes and quality of life for people with epilepsy.
Key Takeaways About Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a complex neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Here are some key takeaways:
- Epilepsy can be caused by a variety of factors such as genetic mutations, brain injuries, infections, or tumors.
- It can affect individuals of any age or gender, although certain age groups such as children and older adults are at a higher risk.
- While epilepsy itself is not typically fatal, it can increase the risk of premature death due to accidents or injuries during seizures. This highlights the importance of effective seizure management and prevention.
- Greater awareness and understanding of epilepsy can help reduce stigma and improve outcomes for those living with the condition. This includes educating the public about the causes and symptoms of epilepsy, promoting access to quality care and treatment options, and supporting research into new treatments and interventions.
- People with epilepsy can live full and productive lives with proper management and support. This may involve working closely with healthcare providers to develop an individualized treatment plan, making lifestyle modifications such as getting enough sleep and avoiding triggers, and building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare professionals.
By increasing our understanding of epilepsy and working together to address its challenges and gaps in care, we can improve outcomes for people with epilepsy and their families.
